


EnCor Biotechnology
Mouse Monoclonal Antibody to FOX3/NeuN (Rbfox3, Hrnbp3, A6nfn3), Cat# MCA-1B7
Description
The MCA-1B7 antibody was raised against a recombinant human FOX3 construct based only on the N-terminal sequence. FOX3 is also known as NeuN, a well established and widely used neuronal marker originally defined by the A60 antibody from Millipore-Sigma. We found that the peptide YPPAQYPPPPQNGIPAEYAP, amino acids 5-24 of FOX3, inhibits binding of both MCA-1B7 and A60 to recombinant human FOX3. The central 10 amino acids of the peptide is likely the most significant component of the MCA-1B7 and A60 epitopes (see here for details). Our antibody works well for western blotting and for IF, ICC and IHC (see data under "Additional Info" tab). The equilibrium dissociation constant (KD) is 2.69 x 10-9M for MCA-1B7, significantly higher affinity than A60, which has a KD of 7.95 x 10-9M under identical conditions. The same recombinant immunogen generated goat, rabbit and chicken polyclonal antibodies to FOX3/NeuN, GPCA-FOX3, RPCA-FOX3 and CPCA-FOX3 respectively. These antibodies also work in the same way as MCA-1B7 and A60 and can be used in double and triple staining protocols on mouse model tissues on which mouse monoclonal antibodies present technical problems. The antibody can also be used to determine the content of neurons versus glia in different CNS regions (6,7)
- Cell Type Marker
- Developmental Marker
- Epitope Mapped Antibodies
- Immunohistochemistry Verified
- Mouse Monoclonal Antibodies
- Our Most Widely Used Reagents
Add a short description for this tabbed section
| Immunogen: | N-terminal 99 amino acids of human FOX3 expressed in and purified from E. coli |
| HGNC Name: | RBFOX3 |
| UniProt: | A6NFN3 |
| Molecular Weight: | 46, 48kDa |
| Host: | Mouse |
| Isotype: | IgG2b heavy, κ light |
| Species Cross-Reactivity: | Human, Rat, Mouse |
| RRID: | AB_2572267 |
| Format: | Protein G affinity purified antibody at 1mg/mL in 50% PBS, 50% glycerol plus 5mM NaN3 |
| Applications: | WB, IF/ICC, IHC |
| Recommended Dilutions: | WB: 1:20,000-1:50,000. IF/ICC, and IHC: 1:2,000-1:5,000 |
| Storage: | Store at 4°C for short term, for longer term store at -20°C. Stable for 12 months from date of receipt. |
In the early 90s an unusual protocol resulted in the raising of a mouse monoclonal antibody, clone A60, against a component of neuronal nuclei and proximal perikarya (1). The component was therefore named "NeuN" and was shown to correspond to two protein bands at 46 and 48kDa on western blots. The antibody become very widely used as a reliable neuronal marker, apparently binding to neurons in all vertebrates, and athough a few neuronal cell types were not recognized such as cerebellar Purkinje cells, olfactory mitral cells and many type of retinal neuron, NeuN immunoreactivity has been widely used to identify neurons. The identity of the NeuN protein was unknown until 2009 when Kim et al. (2) showed that it was identical to FOX3, a mammalian homolog of a gene product originally identified in C. elegans and named FOX1 (2,3). There are three mammalian homologs, FOX1, FOX2 and FOX3, which are believed to have a role in the regulation of mRNA splicing (4). All three contain an almost identical central RNA recognition motif or RRM domain, a region of about 90 amino acids found in numerous proteins which in all three molecules specifically binds the hexaribonucleotide UGCAUG (4). Four protein isoforms of FOX3 result from alternate splicing of two exons from the single gene which code for an insert close to the C-terminus and a short C-terminal extension (5). The extension includes a C-terminal proline-tyrosine sequence preceded by hydrophobic amino acids (Φ-PY) which is known to function in nuclear localization, apparently accounting for FOX3 being present in both nuclei and cytoplasm in certain neurons.
This antibody has become widely used sold by EnCor and through our numerous OEM partners, and information on this can be viewed using Google scholar by searching for "1B7 AND (NeuN or FOX3)" or by selecting here. Here is a CiteAb link to peer reviewed publications which use this antibody obtained directly from EnCor, here.

Above: Chromogenic immunostaining of a formalin fixed paraffin embedded rat hippocampus section with mouse mAb to FOX3/NeuN, 1mg/mL MCA-1B7, dilution 1:2,000, detected in DAB (brown) following the Vector Labs immPRESS® method with citrate retrieval. Hematoxylin (blue) was used as the counterstain. This antibody has also been validated on NBF fixed human tissues. Mouse select image for larger view.

Above: Binding curve set for MCA-1B7 (25nM IgG) and limiting dilutions of recombinant FOX3 peptide (0-500nM) obtained using our in-house label-free bio-layer interferometry system (Octet RED96). Color-coded traces show sensorgram data normalized to baseline after subtraction of 0nM IgG signal from all channels. Traces with overlying fit lines in red indicate their inclusion in the global fit analysis used to derive kinetic parameters listed under the legend (R^2 - goodness of correlation between the fit and data; kon - association rate constant; koff - dissociation rate constant; KD = koff/kon - affinity constant/equilibrium dissociation constant; see EnCor’s validation pipeline for more details). Mouse click on the image to get an enlarged view.
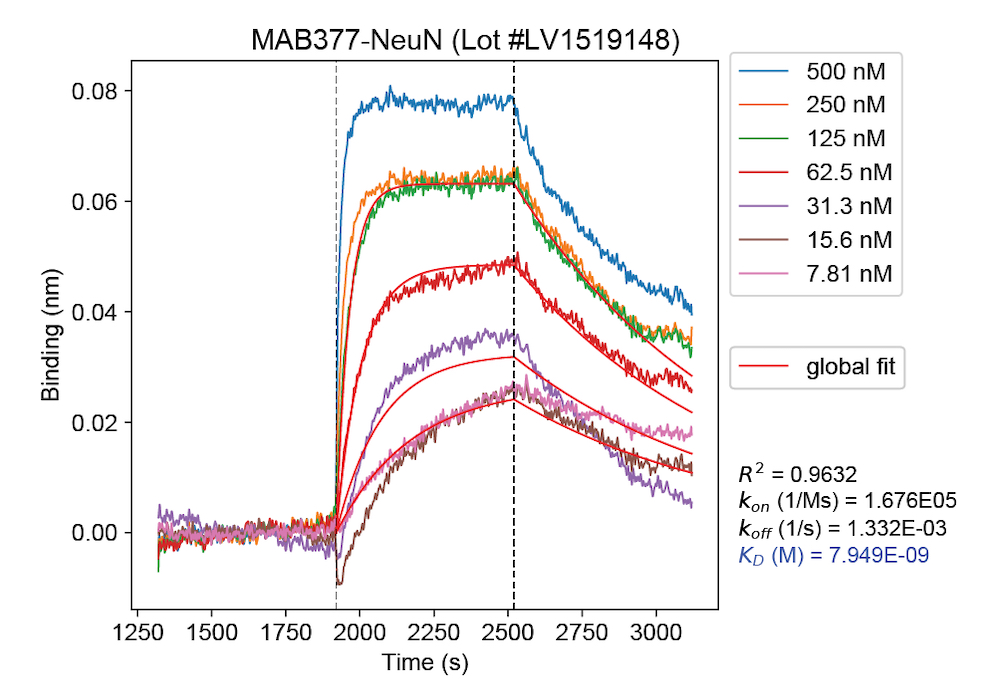
Above: Binding curve set for the Millipore mouse monoclonal antibody MAB377 (25nM IgG) and limiting dilutions of recombinant FOX3 peptide (0-500nM) obtained using our in-house label-free bio-layer interferometry system (Octet RED96). Color-coded traces show sensorgram data normalized to baseline after subtraction of 0nM IgG signal from all channels. Traces with overlying fit lines in red indicate their inclusion in the global fit analysis used to derive kinetic parameters listed under the legend (R^2 - goodness of correlation between the fit and data; kon - association rate constant; koff - dissociation rate constant; KD = koff/kon - affinity constant/equilibrium dissociation constant; see EnCor’s validation pipeline for more details). Mouse click on the image to get an enlarged view.
1. Mullen RJ, Buck CR, Smith AM. NeuN, a neuronal specific nuclear protein in vertebrates. Development 116:201-11 (1994).
2. Hodgkin J, Zellan JD, Albertson DG. Identification of a candidate primary sex determination locus, fox-1, on the X chromosome of Caenorhabditis elegans. Development 120:3681-3689 (1994).
3. Kim KK, Adelstein RS, Kawamoto S. Identification of neuronal nuclei (NeuN) as Fox-3, a new member of the Fox-1 gene family of splicing factors. J. Biol. Chem. 284:31052-61 (2009).
4. Underwood JG, et al. Homologues of the Caenorhabditis elegans Fox-1 protein are neuronal splicing regulators in mammals. Mol. Cell Biol. 25:10005-16 (2005).
5. Dredge BK, Jensen KB. NeuN/Rbfox3 nuclear and cytoplasmic isoforms differentially regulate alternative splicing and nonsense-mediated decay of Rbfox2. PLoS One doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0021585 (2011).
6. Herculano-Houzel S, Lent R. Isotropic fractionator: a simple, rapid method for the quantification of total cell and neuron numbers in the brain. J. Neurosci. 25:2518-2521 (2005).
7. Azevedo FA. et al. Equal numbers of neuronal and nonneuronal cells make the human brain an isometrically scaled-up primate brain. J. Comp. Neurol. 513:532-41 (2009).
Add a short description for this tabbed section





